Welcome to a fascinating journey through the evolution of ERP systems. In this article, we will explore the ERP life cycle, from its humble beginnings to the sophisticated systems we use today. Understanding the evolution of ERP systems is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their operations and stay ahead of the competition. So, sit back, relax, and let’s dive into the world of ERP systems.
Introduction to ERP Life Cycle
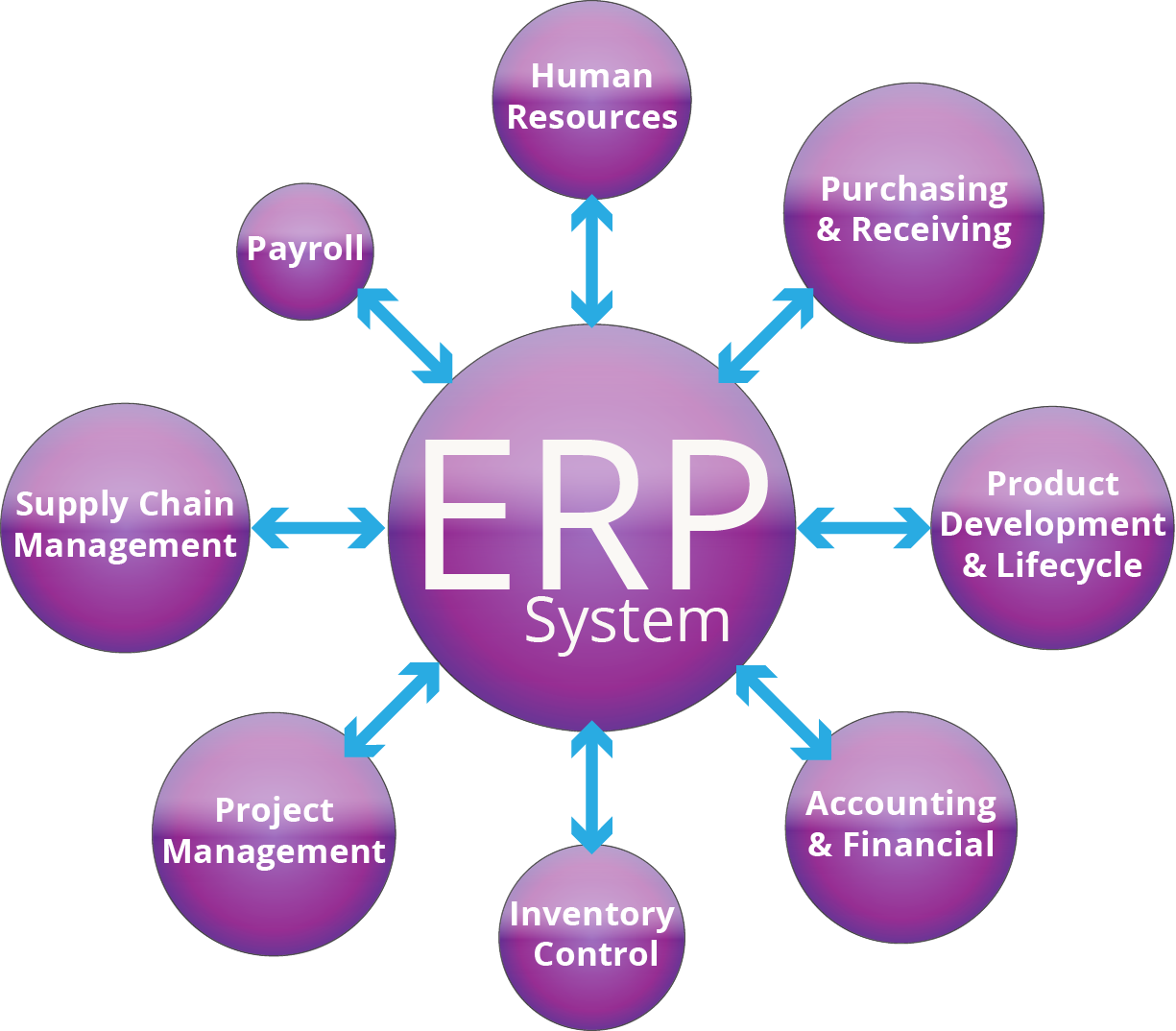
ERP Life Cycle refers to the various stages that an ERP system goes through from conception to retirement. This life cycle consists of several important phases that are crucial for the successful implementation and maintenance of an ERP system within an organization.
The first phase of the ERP life cycle is the Planning stage. During this phase, organizations identify the need for an ERP system and define their requirements. They conduct a thorough analysis of their current processes and systems to determine how an ERP system can help streamline operations and improve efficiency. This phase also involves setting goals and objectives for the ERP implementation, as well as establishing a budget and timeline for the project.
Once the planning phase is complete, organizations move on to the Selection phase. In this stage, they evaluate different ERP vendors and products to find the solution that best meets their needs. This involves researching different vendors, attending product demonstrations, and gathering feedback from other organizations that have implemented similar systems. The goal of the Selection phase is to choose an ERP system that aligns with the organization’s goals and can be implemented within the established budget and timeline.
After selecting an ERP system, organizations enter the Implementation phase. This phase involves installing the ERP software, configuring it to meet the organization’s requirements, and migrating data from existing systems to the new ERP system. Implementation also involves training employees on how to use the new system effectively and making any necessary adjustments to ensure a smooth transition. This phase is crucial for the successful adoption of the ERP system and requires careful planning and coordination between different teams within the organization.
Once the ERP system is up and running, organizations enter the Maintenance phase of the ERP life cycle. During this phase, organizations monitor the performance of the ERP system, address any issues that arise, and make updates and enhancements as needed. This phase also involves providing ongoing training and support to employees to ensure they are using the system efficiently. Maintenance is an ongoing process that requires continuous attention to ensure the ERP system is meeting the organization’s needs and delivering the expected benefits.
The final phase of the ERP life cycle is the Retirement phase. This phase occurs when an organization decides to replace their current ERP system with a new solution or when the system becomes obsolete. Retirement involves decommissioning the old ERP system, migrating data to the new system, and ensuring a smooth transition for employees. It also involves evaluating the lessons learned from the current ERP system implementation and using that knowledge to inform future ERP projects within the organization.
Overall, the ERP life cycle is a comprehensive framework that guides organizations through the process of implementing and managing an ERP system. By following the stages of the ERP life cycle, organizations can maximize the benefits of their ERP system and ensure its success in improving efficiency and productivity within the organization.
Planning and Selection of ERP System
When embarking on the journey of implementing an ERP system, it is crucial to spend adequate time planning and selecting the right system for your organization. This is a vital step that can impact the success of your ERP implementation project.
First and foremost, it is important to clearly define your organization’s goals and objectives for implementing an ERP system. This will help guide your selection process and ensure that the chosen system aligns with your business needs. Consider factors such as scalability, industry-specific requirements, budget constraints, and overall business strategy when determining your ERP requirements.
Next, research and evaluate different ERP systems that are available in the market. There are various ERP vendors that offer systems tailored to specific industries and company sizes. It is important to assess the features and functionalities of each system to determine which one best meets your requirements. Additionally, consider the vendor’s reputation, customer support services, and implementation success rate when making your selection.
It is also essential to involve key stakeholders from different departments in the planning and selection process. This will ensure that the chosen ERP system addresses the needs of all departments and is well-received by end-users. Collaborating with stakeholders will also help build buy-in and support for the ERP implementation project.
Furthermore, consider the implementation timeline and resources required for each ERP system. Some systems may require longer implementation periods or additional resources, which can impact your organization’s operations and budget. It is important to have a clear understanding of the implementation process, including training and support services provided by the vendor.
Finally, create a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and responsibilities for each phase of the project. This plan should also include a contingency strategy in case of unexpected challenges or delays during the implementation process. Communicate regularly with stakeholders and keep them informed of the progress to maintain transparency and accountability throughout the project.
In conclusion, the planning and selection of an ERP system is a critical step in ensuring the success of your ERP implementation project. By taking the time to define your organization’s goals, research and evaluate different systems, involve key stakeholders, and create a detailed implementation plan, you can set your project up for success and maximize the benefits of your new ERP system.
Implementation of ERP System
Implementing an ERP system is a crucial step towards streamlining business processes and improving overall efficiency. The implementation process typically involves several key phases that are essential for the successful deployment of the ERP system. These phases include planning, design, deployment, testing, training, and maintenance.
During the planning phase, the organization needs to define its objectives and goals for implementing the ERP system. This involves assessing the current business processes, identifying areas that need improvement, and determining the key functionalities required in the ERP system. It is essential to involve key stakeholders from different departments in this phase to ensure that the system will meet the needs of the entire organization.
Once the planning phase is complete, the next step is the design phase, where the organization works with the ERP vendor to customize the system according to its specific requirements. This includes mapping out the business processes, configuring the system, and setting up user permissions. It is important to ensure that the system is aligned with the organization’s workflows and that it can support future growth and scalability.
After the design phase is completed, the system is deployed and rolled out to the end users. This involves installing the software, migrating data from the old system to the new system, and integrating the ERP system with other third-party applications if necessary. It is crucial to have a well-defined deployment plan in place to minimize disruption to the business operations during the transition period.
Testing is a critical phase in the implementation process as it helps identify any issues or bugs in the system before it goes live. This involves conducting various tests such as system integration testing, user acceptance testing, and performance testing to ensure that the ERP system functions as expected. Any issues that are identified during testing should be addressed and resolved promptly to prevent them from impacting the system post-implementation.
Training is another essential aspect of ERP system implementation as it ensures that end users are familiar with the system and can effectively use it in their day-to-day tasks. Training programs should be tailored to the needs of different user groups within the organization, providing them with the knowledge and skills required to effectively utilize the ERP system. This helps maximize user adoption and ensures that the organization can derive maximum value from the system.
After the ERP system is successfully implemented, it is important to have a maintenance plan in place to ensure that the system continues to operate smoothly and efficiently. This involves regularly monitoring the system performance, conducting periodic updates and patches, and providing ongoing support and training to users. By following a structured approach to ERP system implementation and post-implementation support, organizations can effectively leverage the benefits of the system and drive business growth.
Training and User Adoption
Training and user adoption are crucial components of the ERP life cycle. Proper training ensures that employees know how to use the system effectively and efficiently, leading to a smoother transition and increased productivity. User adoption refers to the degree to which employees embrace the new ERP system and make it a part of their daily work routine.
Training should begin early in the implementation process to familiarize employees with the new system and its functionalities. This will help to alleviate any fears or resistance to change that may arise. Different training methods should be used depending on the needs and preferences of the employees. Some may prefer hands-on training while others may prefer video tutorials or self-paced online courses.
It is important for training to be ongoing, even after the ERP system has been fully implemented. This will help to ensure that employees continue to learn new features and functionalities of the system as updates and upgrades are released. Training sessions should be organized regularly to reinforce learning and address any questions or issues that may arise.
In addition to formal training sessions, user adoption can be fostered through various means such as creating a positive user experience, providing adequate support and resources, and encouraging collaboration and communication among employees. User feedback should be encouraged and taken into consideration to improve the system and make it more user-friendly.
One effective way to promote user adoption is to designate super users within each department or team who can serve as champions for the new system. These super users can provide support and assistance to their colleagues, answer questions, and provide feedback to the IT team. They can also help to identify any training needs or gaps in knowledge among employees.
Another important aspect of user adoption is management buy-in and support. Managers and leaders should lead by example and demonstrate their commitment to the new system. They should encourage and motivate their teams to embrace the change and make the most of the new ERP system. Managers should also be open to feedback and suggestions from employees to ensure that the system is meeting their needs and improving their workflows.
In conclusion, training and user adoption are critical to the success of an ERP implementation. By investing in proper training and fostering user adoption, organizations can ensure that their employees are proficient in using the system and that they are fully engaged and committed to making the new ERP system a success.
Maintenance and Upgrades of ERP System
Once an ERP system is implemented, it is crucial to continuously maintain and update it to ensure its optimal performance. Maintenance involves monitoring the system regularly to identify any issues or problems that may arise. This can include ensuring data accuracy, system backups, and security measures are up to date. Regular maintenance helps prevent system breakdowns and ensures smooth operations.
Upgrades are essential for keeping an ERP system current and taking advantage of new features and functionalities. Technology is constantly evolving, and new updates may be released to improve the system’s efficiency and effectiveness. Upgrades can involve installing new software versions, patches, or modules to enhance the system’s capabilities.
Before implementing any upgrades, it is important to thoroughly test them in a controlled environment to minimize disruption to daily operations. This can involve creating a test environment that mirrors the production system to validate the changes before deploying them live. Testing helps identify any potential issues or conflicts that may arise during the upgrade process.
Communication is key when it comes to maintenance and upgrades. All stakeholders, including end-users, IT staff, and management, should be informed about any upcoming changes to the system. Providing training and support to end-users can help smooth the transition and ensure they are comfortable with any new features or functionalities.
Regular training sessions can also help employees adapt to system changes and improve their proficiency in using the ERP system. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency in daily operations. Additionally, ongoing support and troubleshooting resources should be available to address any issues that may arise post-upgrade.
Overall, maintenance and upgrades are vital components of the ERP system lifecycle. By keeping the system current and ensuring its optimal performance, organizations can maximize the benefits of their ERP investment and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Originally posted 2025-06-17 03:37:45.